- About Us
- Admissions
- Academic Life
- School Life
- Sixth Form
We hope the curriculum allows Year 7 to 11 students to:
The curriculum is designed to build upon the big ideas introduced in Y7 and Y8 to introduce higher level concepts in later years. In addition, to stretch students to prepare them for post-16 science education.
Key Stage 5 science provides a balanced curriculum for those interested in science and prepares them for intellectual and practical challenges of accessing and succeeding in an extensive range of higher education courses.
The Science department is fortunate to have a team of twenty science specialist teachers housed in the Myddelton block comprising 14 specialist science laboratories, supported by an excellent technical team.
The curriculum allows Year 7 to 11 students develop a lifelong interest and curiosity in science and be able to apply scientific ideas, principles and practical skills to their future life as responsible global citizens. To appreciate how human scientific development has impacted the world for better and worse. In addition, to stretch students to prepare them for post-16 science education.
Key Stage 5 science provides a balanced curriculum for those interested in science and prepares them for intellectual and practical challenges of accessing and succeeding in an extensive range of higher education courses.
Academic results are outstanding. Many students go on to study scientific courses at university including medical sciences, dentistry, veterinary science and engineering.
Learning is enhanced by a rich and varied array of extra-curricular activities. There are Science and Crest Clubs and Olympiad competitions to challenge and extend the interests of our students. We run a comprehensive series of Science Society Lectures throughout the year with talks from eminent speakers from the worlds of medicine, engineering, psychology, .
In Key Stage 3 students have three hours of science a week with one teacher in Year 7 before splitting between Biology, Chemistry and Physics teachers in Years 8 and 9. They are offered an enriching curriculum that covers a wide range of scientific concepts as well as equipping them with practical and investigative skills that prepares them to meet the demands of higher level courses and life beyond school. There is an important emphasis on ‘Working scientifically’ – the impact of science on society and how research is carried out and scrutinised to ensure it is valid.
There are two GCSE courses available – Triple science (three GCSEs) and Combined Science Trilogy (two GCSEs). Both specifications cover topics from Biology, Chemistry and Physics as well as ‘working scientifically’. Six GCSE exams are taken at the end of both courses. The majority of students opt to study Triple science GCSE.
Specifications: AQA Combined Science Trilogy 8464, AQA Biology 8461, Chemistry 8462, Physics 8463
Biology, Chemistry and Physics A-level courses are offered in the 6th form.
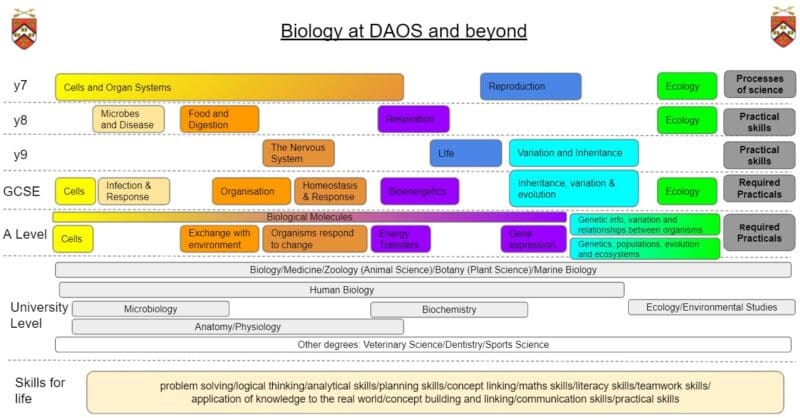
Biology is a fascinating and popular subject in the 6th form, attracting enough students to make four or five teaching groups in each year. Students follow the AQA course; the A Level it is divided into topics covering key biological concepts, ranging from cells to individuals to populations; from the fundamentals of life and inheritance to the newer technologies of genetic engineering and biotechnology; from biochemistry to ecosystems. There are many practical opportunities within the taught course including the exam board required practicals in which students need to demonstrate various competencies and so be awarded practical endorsement alongside their exam grade. There are a number enrichment opportunities.
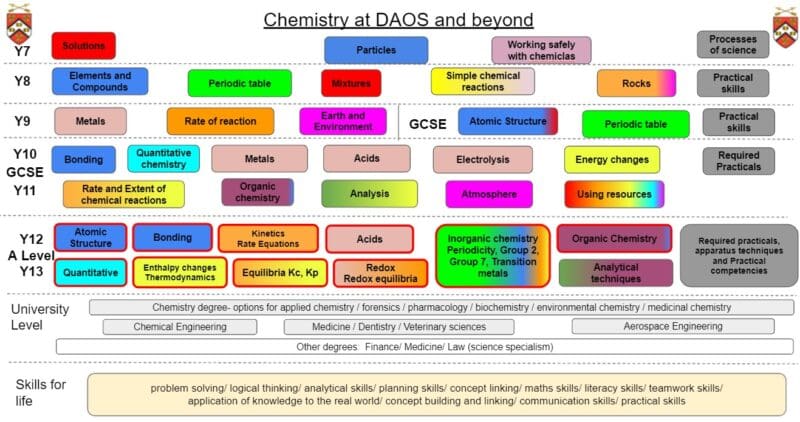
The department follows the AQA specification which is traditional in style, but offers ample opportunity for experimental work. The A-level courses extend and develop the key ideas from GCSE Chemistry and introduce modern concepts. The emphasis of the syllabus is on the relevance of the subject to everyday life and it is therefore an interesting and dynamic course. Year 2 course is a more advanced treatment of the ideas previously studied, building on earlier concepts. There are many experiment opportunities, including the required practicals that contribute towards students achieving practical endorsement.
There are usually four or five A-level groups in each 6th form year group and a significant number of students take part in enrichment activities such as the various competitions set by the Royal Society of Chemistry
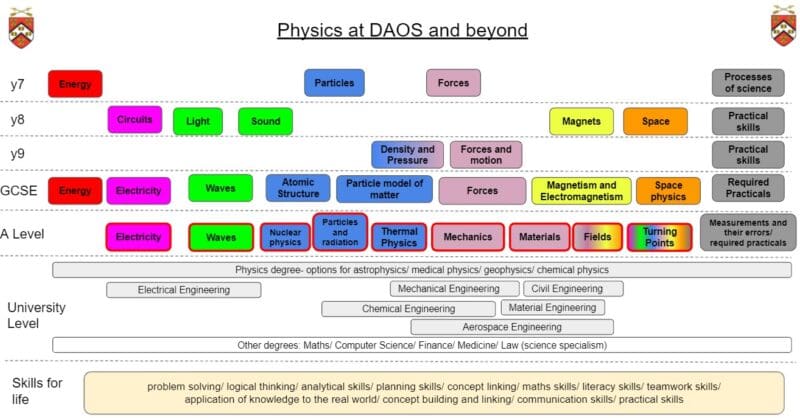
Students follow the AQA Physics A-level. The specification covers classical physics topics such as mechanics and theoretical physics such as special relativity. Students undertake practical work regularly throughout the course and ten of these practicals contribute to the A-Level practical endorsement.
Students are encouraged to participate in the Headstart courses at the end of Year 12, which provide tasters at universities in science and engineering subjects. A visit to CERN, the European Centre for Particle Physics in Geneva takes place most years. Students can also challenge themselves through the Physics Olympiad with the aim of representing Great Britain in the International Physics Olympiad.
Mike Jays – Head of Science
Corinne Doust – Head of Biology
Bernard Davies – Head of Chemistry
Kate Fradley – Head of Physics
| Overview | Students have one science teacher for three lessons a week to introduce the basics of science education and the big ideas that form the foundation of scientific knowledge – energy, forces, particles, organisms. The students are also introduced to working scientifically to understand the practical method to produce valid outcomes. | |||
| Focus | Major Assessments | |||
| Autumn |
Process of science – Lab safety and equipment; Working scientifically and investigation skills – variables, planning, presenting results and graphs, analysis of data; Research project.
Cells and Organ systems – Microscopes; Cells; Cell division; Organisms, organs and organ systems.
Particles – Particle model and applications; Changing state; Conduction, convection and radiation. |
|||
| Spring |
Energy – Energy stores and transfers; Fuels, Power stations and renewables
Reproduction – Reproductive cycle; Puberty; Reproductive systems; Sex cells, fertilisation, menstrual cycle, pregnancy, birth and contraception.
Solutions – Mixtures and filtration; Dissolving and solubility; Evaporation, distillation, chromatography. |
January online assessment (50 minutes) | ||
| Summer |
Ecology – Plant and Animal Kingdoms; Plant variation; Food chains and Pyramids of numbers and mass; Population growth; Conservation.
Forces – Identifying, describing and measuring forces; Friction; Tension; Weight; Balanced and unbalanced forces; Speed and Distance-time graphs.
Working safely with chemicals – Identifying acids and alkalis; Indicators and pH scale; Neutralisation and antacids. |
Summer assessment on topics covered since January. |
||
| Overview | Lessons are more formally taught as science disciplines as lessons are divided into Biology, Chemistry and Physics (one each per week). | ||
| Focus | Major Assessments | ||
| Autumn | Biology |
Respiration – Breathing and gas exchange; Aerobic respiration; Circulation and heart rate; Homeostasis and thermoregulation; Anaerobic respiration; Asthma.
Microbes and disease – Useful microbes; Disease, fighting infection, antibiotics and vaccines; Parasites; Plant defences; Non-communicable diseases. |
December online assessments on each science (30 minutes each) |
| Chemistry |
Elements and Compounds – Atoms and atomic structure; Making and naming compounds; Writing chemical equations.
Periodic table – History and structure; Group 1; Group 7. |
||
| Physics |
Light – Basic light properties; Ray diagrams, Reflection, Refraction, Dispersion, seeing Colour and colour filters.
Circuits – Static electricity, Building and drawing circuits; Current; Voltage; Resistance; Fuses |
||
| Spring | Biology | Food and Digestion– Food groups and malnutrition; Food tests; Digestive system, enzymes, absorption and egestion; Glucoregulation. | |
| Chemistry |
Mixtures – Separating techniques; Simple and Fractional distillation.
Simple chemical reactions – Chemical and Physical changes; Acids and metals; Energy changes, burning fuels and fire safety; Types of chemical reactions and writing chemical equations. |
||
| Physics |
Sound – Making and describing sound; Sound waves, amplitude, wavelength, frequency; Sound through media; Speed of sound.
Magnets – Magnetic materials and magnets; Magnetic fields; Electromagnets. |
||
| Summer | Biology | Ecology – Microscope skills, sampling techniques |
Summer written assessment on topics covered since December. (50 minutes) |
| Chemistry | Rocks – Weathering and Rock cycle; Sedimentary, Igneous and Metamorphic rocks; Earth movements. | ||
| Physics | Space – Earth days and years; Moon phases; Seasons; Solar system and beyond; Weight and mass. | ||
| Overview |
Students have three science lessons – one in each science. The KS3 curriculum is completed mid-way through the year. The GCSE course (AQA) starts being delivered at February half term. |
||
| Focus | Major Assessments | ||
| Autumn | Biology | Life – Biodiversity; Photosynthesis; Transpiration; Starch; Plant reproduction and seed dispersal; Carbon cycle | |
| Chemistry |
Metals – Reactivity series; Displacement reactions; Metal extraction; Acids and Bases reactions.
Rates of reaction: Collision theory; Factors that affect rate of reaction |
||
| Physics | Forces and their effects – Identifying and drawing forces; Resultant force, drag and terminal velocity; Speed and distance-time graphs | ||
| Spring 1 | Biology | Variation and Inheritance – Genes, Selective breeding; Cloning |
Mid-year assessment based on all KS3 Yr9 topics |
| Chemistry | Earth and the Environment – Recycling; Acid rain; Climate change | ||
| Physics | Physics in context: States of matter and density; pressure; turning effects and moments | ||
| Spring 2 |
STUDENT OPTIONS – initial selection of GCSE science course based upon interest, achievement and teacher advice. ALL PUPILS START GCSE COURSE –No difference between Combined or Triple science |
||
| Biology | 1. Cells | ||
| Chemistry | 1.1 Atomic structure | ||
| Physics | Energy part 1 | ||
| Summer | Biology | 1. Cells (continued) | Summer assessment (40 minutes per science) based on opening GCSE topics |
| Chemistry | 1.2 Periodic table | ||
| Physics |
Electricity part 1 Mains electricity and energy transfers |
||
GCSE science course confirmed in light of progress in opening GCSE topics
| Overview |
Specification: AQA Combined Science Trilogy 8464 Students have six science lessons per week – two in each discipline. Having started the GCSE course in Year 9, the aim is to complete the material needed for Paper 1 by the end of Year 10 and Paper 2 by Easter of Year 11. Biology and Chemistry roughly follow the order of the topics listed in the specification, with tweaks that consider accessibility, development of practical skills (including required practicals) and allow for retrieval learning. In Physics, there is a spiral curriculum that means topics are revisited a number of times over the year to allow embedding of concepts. |
||
| Focus | Major Assessments | ||
| Y10 Autumn Combined | Biology |
2. Organisation 3. Infection and Response |
November assessment (¾ hour) in each science. |
| Chemistry |
1. Atomic structure and Periodic table review 4.1 Metals 2. Bonding and structure |
||
| Physics |
Particle model part 1 Atomic structure part 1 Electricity part 2 |
||
| Y10 Spring Combined | Biology | 4. Bioenergetics |
Mid year assessments (¾ hour) in each science |
| Chemistry |
2. Bonding and Structure cont. 4.2 Acids 4.3 Electrolysis |
||
| Physics |
Particle model part 2 Atomic structure part 2 Energy part 2 |
||
| Y10 Summer Combined | Biology | 7. Ecology |
GCSE paper 1 higher or foundation tier mock (1¼ hours) in each science |
| Chemistry |
3. Quantitative chemistry 5. Energy changes |
||
| Physics |
Forces part 1 Waves part 1 |
||
| Y11 Autumn Combined | Biology | 5. Homeostasis and response |
October assessments (¾ hour) in each science |
| Chemistry |
6.1. Rate of reaction 7. Organic chemistry 9. Chemistry of the Atmosphere |
||
| Physics |
Forces part 2 Electromagnetism Waves part 2 |
||
| Y11 Spring Combined | Biology | 6. Inheritance, variation and evolution |
January GCSE paper 1 higher or foundation tier mock (1¼ hours) in each science
March – Informal GCSE paper 2 in each science sat over two lessons |
| Chemistry |
8. Chemical analysis 10. Using resources 6.2 Extent of chemical reaction |
||
| Physics | Forces part 3 | ||
| Y11 Summer Combined | Biology |
Revision and Public exams
|
|
| Chemistry | |||
| Physics | |||
| Overview |
Specifications: AQA Biology 8461, Chemistry 8462, Physics 8463 Having started the GCSE course in Year 9, the aim is to complete the material needed for Paper 1 by the end of Year 10 and Paper 2 by Easter of Year 11 . Biology and Chemistry roughly follow the order of the topics listed in the specification, with tweaks that consider accessibility, development of practical skills (including required practicals) and allow for retrieval learning. In Physics, there is a spiral curriculum that means topics are revisited a number of times over the year to allow embedding of concepts. Students who struggle with the pace and demand of Triple sciences may move across to Combined Science. |
||
| Focus | Major Assessments | ||
| Y10 Autumn Triple | Biology |
2. Organisation 3. Infection and Response |
November assessment (¾ hour) in each science. |
| Chemistry |
4.1 Metals 2. Bonding and Structure 4.2 Acids |
||
| Physics |
Particle model part 1 Atomic structure part 1 Electricity part 2 Particle model part 2 |
||
| Y10 Spring Triple | Biology | 4. Bioenergetics |
Mid year assessments (¾ hour) in each science |
| Chemistry |
4.3 Electrolysis 3. Quantitative chemistry |
||
| Physics |
Atomic structure part 2 Energy part 2 Forces part 1 |
||
| Y10 Summer Triple | Biology | 7. Ecology |
GCSE paper 1 higher tier mock (1¾ hours) in each science |
| Chemistry |
5. Energy changes 6.1 Rate of reaction |
||
| Physics |
Waves part 1 Forces part 2 |
||
| Y11 Autumn Triple | Biology | 5. Homeostasis and response |
October assessments (¾ hour) in each science |
| Chemistry |
7. Organic chemistry 9. Chemistry of the Atmosphere 8. Chemical Analysis |
||
| Physics |
Electromagnetism part 1 Waves part 2 Forces part 3 (Momentum) Space Physics |
||
| Y11 Spring Triple | Biology | 6. Inheritance, variation and evolution |
January GCSE paper 1 higher tier mock (1¾ hours) in each science
March – Informal GCSE paper 2 mock sat over two lessons |
| Chemistry |
10. Using resources 6.2 Extent of chemical reaction |
||
| Physics |
Waves part 3 Electromagnetism part 2 Forces part 4 |
||
| Y11 Summer Triple | Biology |
Revision and Public exams |
|
| Chemistry | |||
| Physics | |||
Dame Alice Owen’s School
Dugdale Hill Lane
Potters Bar
Hertfordshire
EN6 2DU
01707 643441
[email protected]
Mon – Fri 8:00A.M. – 5:00P.M.